Hearing Loss |
Causes of Hearing Loss
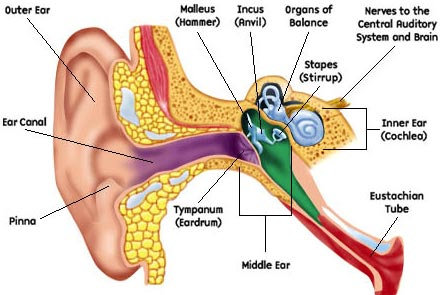
Hearing loss can be caused by problems with the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. Hearing loss resulting from a problem in the outer or middle ear is called a "conductive" hearing loss. Hearing loss from inner ear problem is called a "sensorineural" loss and can be due to impaired inner ear hair cells (sensory) or damaged nerve to the inner ear (neural), or possibly both (sensorineural). A "mixed" loss occurs when both conductive and sensorineural loss is present.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the sensation of ringing or noise in the head. It may occur in association with any type of hearing loss and can be either intermittent or continuous.
Noise Trauma
Noise trauma is a common cause for sensorineural hearing loss. This can be from sudden loud sound such as from shooting a gun, or chronic such as working with loud machinery or driving a vehicle especially with window down. The muffled hearing following noise trauma, especially with tinnitus, are indications that some degree of permanent damage has occurred.
Degree of Hearing Loss
Degree of hearing loss measures the lowest intensity at which sound is apparent, called the patient’s threshold. This is used to determine severity of loss." The following is the classification system used to describe hearing loss:
- Mild hearing loss: unable to hear soft sounds, difficulty understanding speech clearly in noisy environments.
- Moderate hearing loss: unable to hear soft and moderately loud sounds, considerable difficulty understanding speech, particularly with background noise.
- Severe hearing loss: some loud sounds are audible but communication is difficult, without some form of amplification such as a hearing aid.
Profound hearing loss: some extremely loud sounds are audible; a hearing instrument may help communication, but discrimination of sounds may limit understanding. |
| |